The reference value of the dynamic pressure, q
p0, corresponds to the peak speed (wind gusts of a few seconds) , at 10 m above ground level in terrain of 'open country' (category III) type.
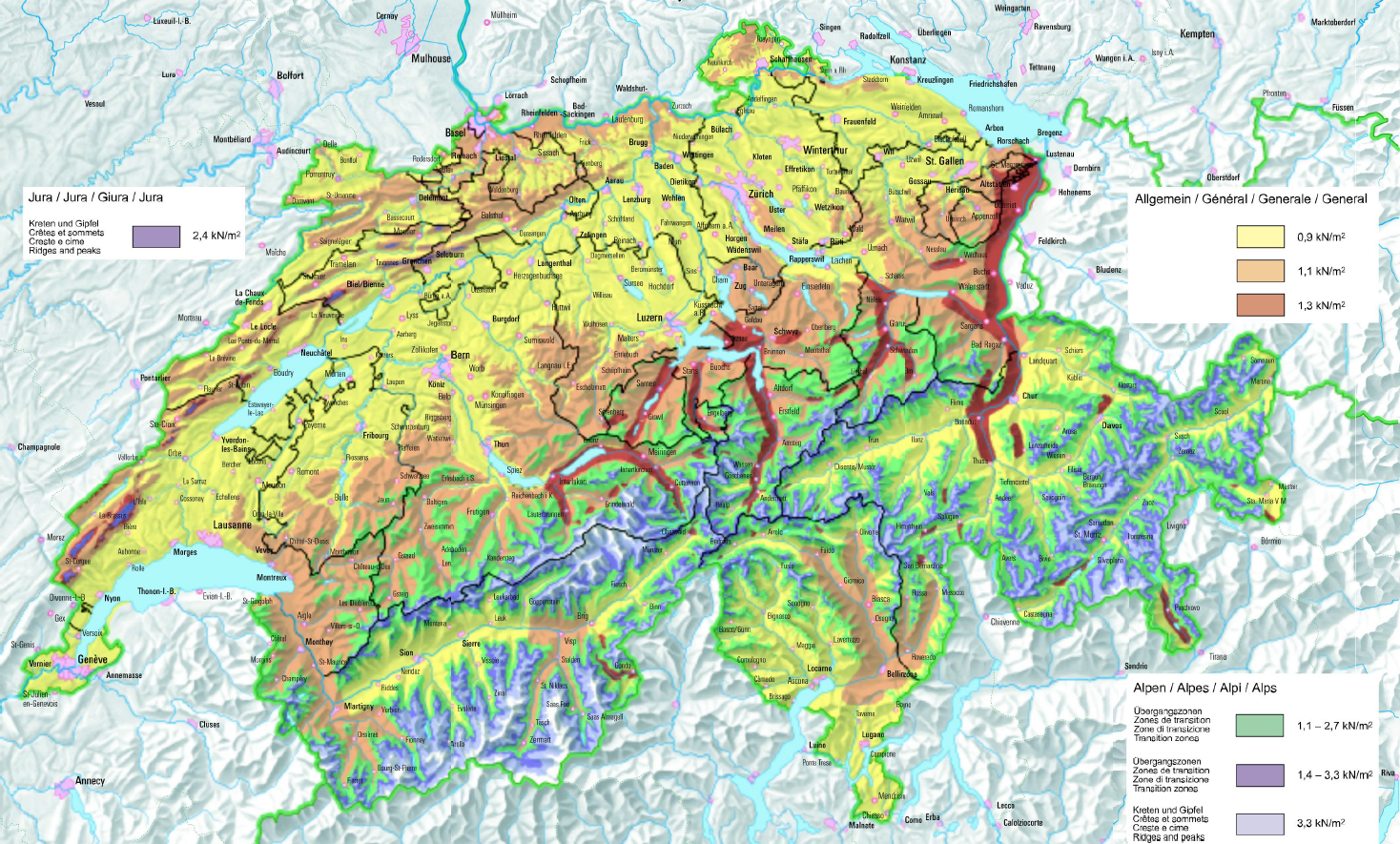
The fundamental values of the dynamic pressure are specified by the Annex E.
This one provides a
country map divided into climatic zones. For the zone
1.1, the specified value of the pressure is: q
p0 =
1.1 kN/m². Probability coefficient of exceeding
The probability p of exceedance is considered on the useful life of the project, itself based on the use of the project.
For our building project, the use is dwelling house, the recommended duration of use, necessary for determining the return period, is therefore 50 years.
The 10 minutes mean wind velocity having the probability p for an annual exceedence is determined by multiplying the basic wind velocity vp by the probability factor of severe wind cprob:
(Not referenced by SIA standards - Application of EN 1991-1-4 Equation 4.2)
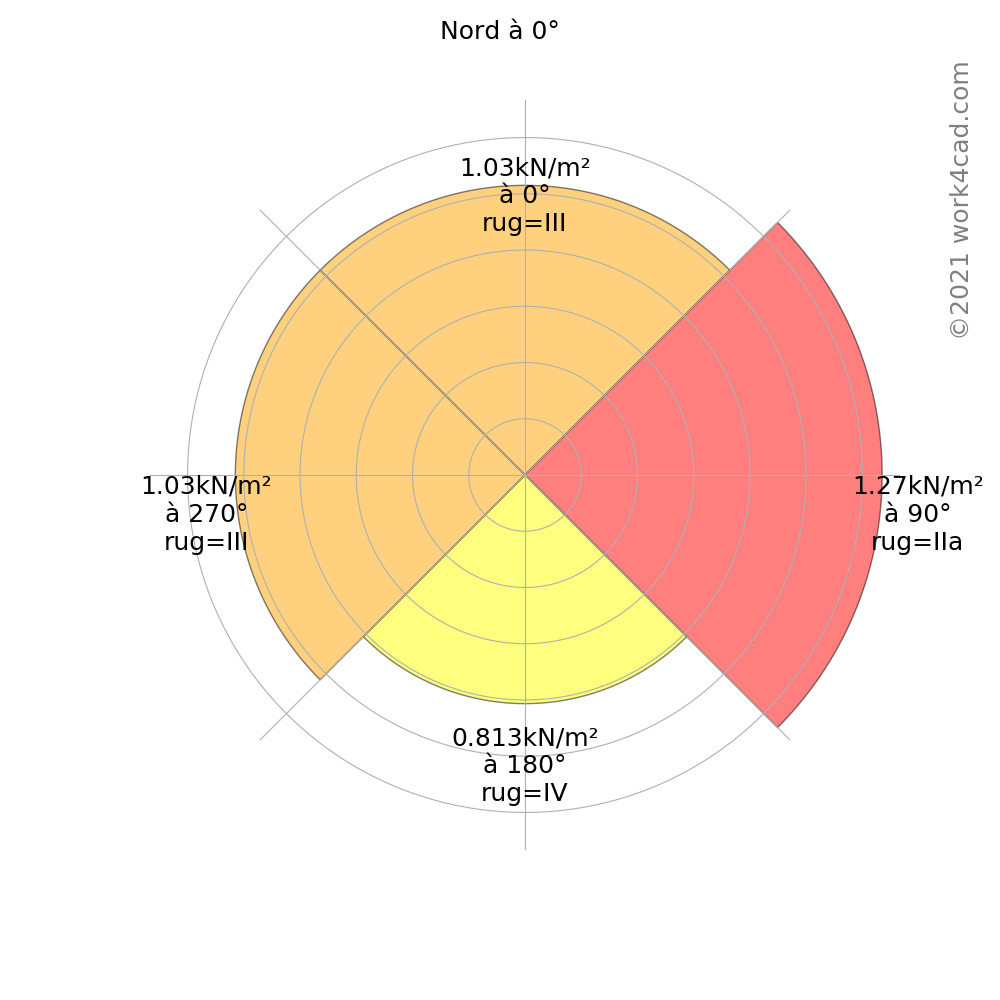
Directional factor of wind
'wind direction' means the direction from which the wind comes.
The SIA standard does not mention a wind direction coefficient to reduce the resulting pressures. We therefore assume that cdir = 1.
Season factor
The SIA standard does not mention a season factor coefficient to reduce the resulting pressures. We therefore assume that cseason = 1.
The peek wind velocity is therefore
(Not referenced by SIA standards - Application of EN 1991-1-4 Equation 4.)